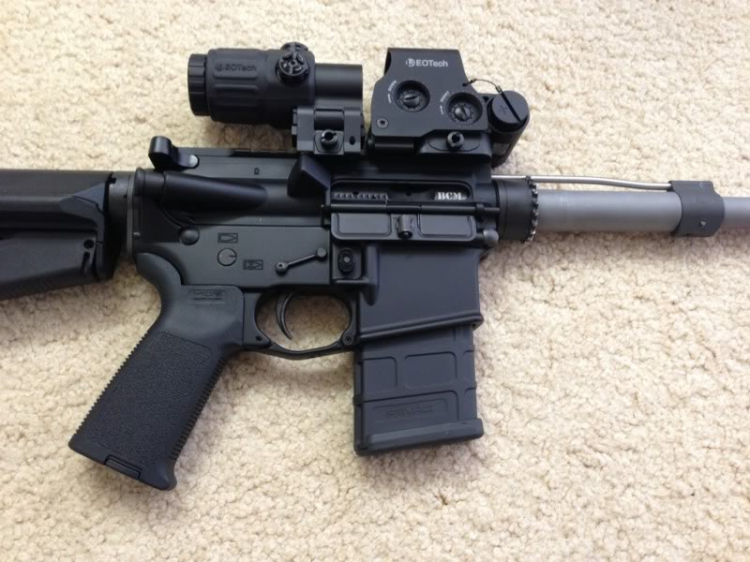
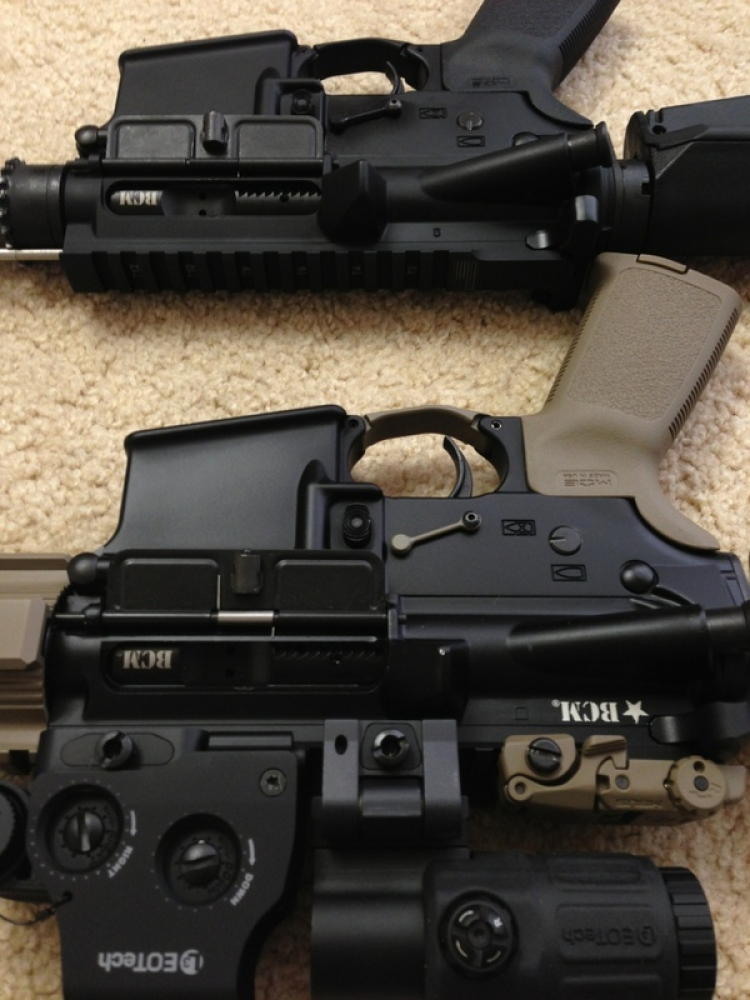
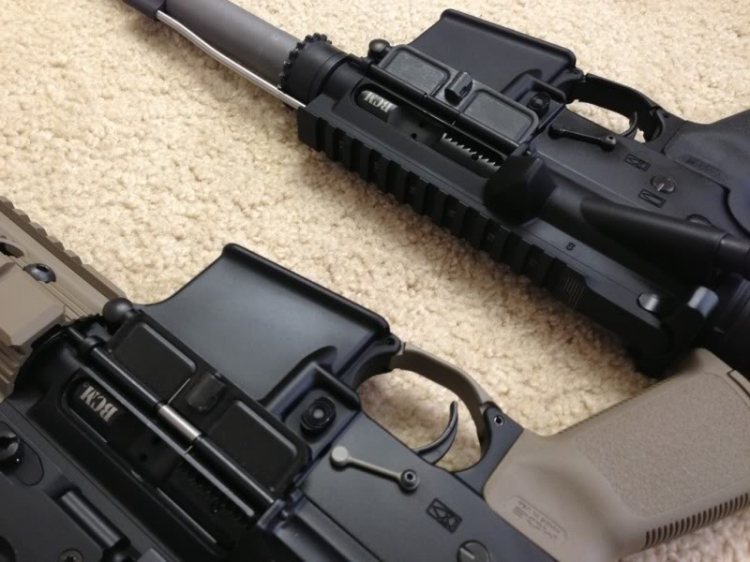
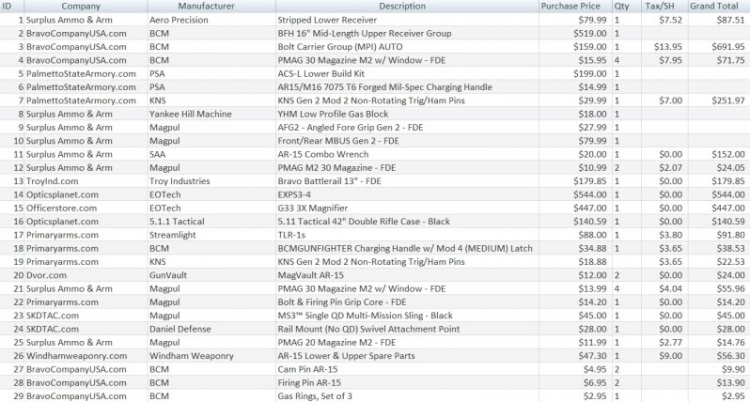
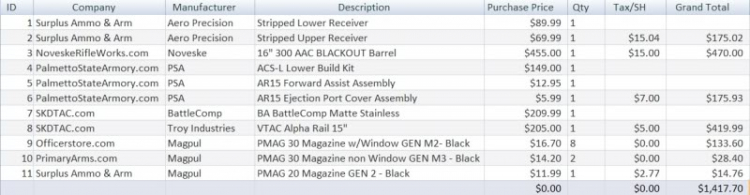
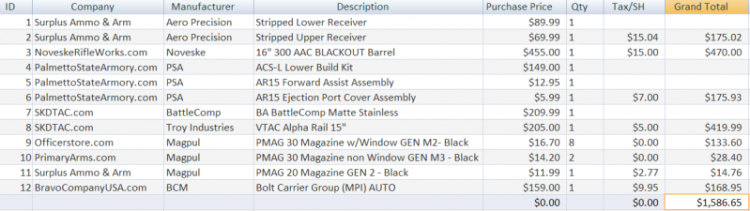
Re:Súng!
QV giỏi thì đọc cái nầy đi:
Operating mechanism
Diagram of an M16 rifle, firing
The main mechanism of operation for the rifle is known as direct gas impingement. Gas is tapped from the barrel as the bullet moves past a gas port located above the rifle's front sight base. The gas rushes into the port and down a gas tube, located above the barrel, which runs from the front sight base into the AR-15's upper receiver. Here, the gas tube protrudes into a "gas key" (bolt carrier key) which accepts the gas and funnels it into the bolt carrier.
The bolt and bolt carrier together form a piston, which is caused to expand as the cavity in the bolt carrier fills with high pressure gas. The bolt is locked into the barrel extension, so this expansion forces the bolt carrier backward a short distance in line with the stock of the rifle to first unlock the bolt. As the bolt carrier moves toward the butt of the gun, the bolt cam pin, riding in a slot on the bolt carrier, forces the bolt to turn and unlock from the barrel extension. (The gas system only serves to unlock the bolt while the projectile has long exited the barrel). Once the bolt is fully unlocked it begins its rearward movement along with the bolt carrier. The bolt's rearward motion extracts the empty cartridge case from the chamber, and as soon as the neck of the case clears the barrel extension, the bolt's spring-loaded ejector forces it out the ejection port in the side of the upper receiver. The bolt is much heavier than the projectile, and along with the recoil-spring pressure inside the stock buffer-tube performs the cartridge ejection function and chambers the following cartridge.
Đại khái là cái ống gas nầy sẽ unlock bolt carrier và làm nó move về phía sau động tác nầy sẽ :
- kéo võ đạn ra khỏi nòng súng
- lên cò
- nạp đạn mới khi bolt carrier chạy về phía trước
Hay
QV giỏi thì đọc cái nầy đi:
Operating mechanism
Diagram of an M16 rifle, firing
The main mechanism of operation for the rifle is known as direct gas impingement. Gas is tapped from the barrel as the bullet moves past a gas port located above the rifle's front sight base. The gas rushes into the port and down a gas tube, located above the barrel, which runs from the front sight base into the AR-15's upper receiver. Here, the gas tube protrudes into a "gas key" (bolt carrier key) which accepts the gas and funnels it into the bolt carrier.
The bolt and bolt carrier together form a piston, which is caused to expand as the cavity in the bolt carrier fills with high pressure gas. The bolt is locked into the barrel extension, so this expansion forces the bolt carrier backward a short distance in line with the stock of the rifle to first unlock the bolt. As the bolt carrier moves toward the butt of the gun, the bolt cam pin, riding in a slot on the bolt carrier, forces the bolt to turn and unlock from the barrel extension. (The gas system only serves to unlock the bolt while the projectile has long exited the barrel). Once the bolt is fully unlocked it begins its rearward movement along with the bolt carrier. The bolt's rearward motion extracts the empty cartridge case from the chamber, and as soon as the neck of the case clears the barrel extension, the bolt's spring-loaded ejector forces it out the ejection port in the side of the upper receiver. The bolt is much heavier than the projectile, and along with the recoil-spring pressure inside the stock buffer-tube performs the cartridge ejection function and chambers the following cartridge.
Đại khái là cái ống gas nầy sẽ unlock bolt carrier và làm nó move về phía sau động tác nầy sẽ :
- kéo võ đạn ra khỏi nòng súng
- lên cò
- nạp đạn mới khi bolt carrier chạy về phía trước
Hay